Late yesterday the Air Resources Board unanimously approved cap-and-trade regulations as part of an on-going effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions which are contributing to climate change. This landmark set of air pollution controls is the first in the nation to be implemented at the state level. The regulations were originally brought to the board in 2008, and have undergone extensive refinement admidst major opposition from big business.
Cap-and-trade is the centerpiece of AB 32, California’s historic climate change law that mandates a reduction in carbon pollution to 1990 levels by 2020. Beginning in 2013 the state’s largest carbon emitters will be required to meet the caps or buy credits if they cannot.
A second phase of compliance begins in 2015 and is expected to include 85% of California’s emissions sources.
Gary Geo, President of Los Angeles-based Climate Action Reserve spoke on how influential this legislation might be for the rest of the nation, “People watch what California does and do emulate it. Future cap-and-trade programs are going to pick up a lot of the design features we are implementing here. You’ll see regional programs develop. They will put pressure on the federal government. It will send out ripples around the country.”
How does the program work?
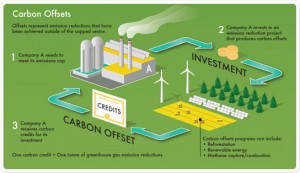 Emissions caps were established after extensive research and benchmarking efforts by a team of scientists. After program implementation businesses will be allowed to reach up to 90% of that established level for emissions. Companies that can reduce their emissions below that level within one year may then sell the excess carbon allowance on the market, thus enabling those companies who are not able to reduce their own emissions to purchase offsets or credits.
Emissions caps were established after extensive research and benchmarking efforts by a team of scientists. After program implementation businesses will be allowed to reach up to 90% of that established level for emissions. Companies that can reduce their emissions below that level within one year may then sell the excess carbon allowance on the market, thus enabling those companies who are not able to reduce their own emissions to purchase offsets or credits.
Read the full press release from the Air Resources Boards website.








